Merge Sort - Data Structure and Algorithms Tutorials
Merge sort is defined as a sorting algorithm that works by dividing an array into smaller subarrays, sorting each subarray, and then merging the sorted subarrays back together to form the final sorted array.
In simple terms, we can say that the process of merge sort is to divide the array into two halves, sort each half, and then merge the sorted halves back together. This process is repeated until the entire array is sorted.
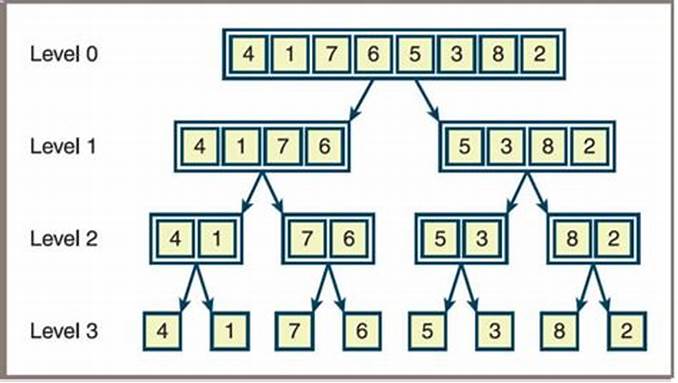
How does Merge Sort work?
Merge sort is a recursive algorithm that continuously splits the array in half until it cannot be further divided, i.e., the array has only one element left (an array with one element is always sorted). Then the sorted subarrays are merged into one sorted array.
Complexity Analysis of Merge Sort:
Time Complexity: O(N log(N)) - Merge Sort is a recursive algorithm and time complexity can be expressed as following recurrence relation.
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + θ(n)
The above recurrence can be solved either using the Recurrence Tree method or the Master method. It falls in case II of the Master Method, and the solution of the recurrence is θ(N log(N)). The time complexity of Merge Sort is θ(N log(N)) in all 3 cases (worst, average, and best) as Merge Sort always divides the array into two halves and takes linear time to merge two halves.
Auxiliary Space: O(N) - In Merge Sort, all elements are copied into an auxiliary array. So, N auxiliary space is required for Merge Sort.
Applications of Merge Sort:
- Sorting large datasets: Merge sort is particularly well-suited for sorting large datasets due to its guaranteed worst-case time complexity of O(n log n).
- External sorting: Merge sort is commonly used in external sorting, where the data to be sorted is too large to fit into memory.
- Custom sorting: Merge sort can be adapted to handle different input distributions, such as partially sorted, nearly sorted, or completely unsorted data.
- Inversion Count Problem
Advantages of Merge Sort:
- Stability: Merge sort is a stable sorting algorithm, which means it maintains the relative order of equal elements in the input array.
- Guaranteed worst-case performance: Merge sort has a worst-case time complexity of O(N log(N)), which means it performs well even on large datasets.
- Parallelizable: Merge sort is a naturally parallelizable algorithm, which means it can be easily parallelized to take advantage of multiple processors or threads.
Drawbacks of Merge Sort:
- Space complexity: Merge sort requires additional memory to store the merged sub-arrays during the sorting process.
- Not in-place: Merge sort is not an in-place sorting algorithm, which means it requires additional memory to store the sorted data. This can be a disadvantage in applications where memory usage is a concern.
- Not always optimal for small datasets: For small datasets, Merge sort has a higher time complexity than some other sorting algorithms, such as insertion sort. This can result in slower performance for very small datasets.
Comparison of Merge Sort, Quick Sort, and Bubble Sort
| Sorting Algorithm | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Stability | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Merge Sort | O(N log(N)) | O(N) | Stable | Sorting large datasets, external sorting, custom sorting, inversion count problem |
| Quick Sort | O(N^2) (worst case), O(N log(N)) (average case) | O(log(N)) (worst case), O(N) (average case) | Not stable | General-purpose sorting, widely used in practice |
| Bubble Sort | O(N^2) | O(1) | Stable | Not suitable for large datasets, primarily used for educational purposes |
Top 20 Interview Questions on Merge Sort
| Question | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|
| What is Merge Sort, and how does it work? | Beginner |
| Explain the time complexity of Merge Sort. | Beginner |
| What is the space complexity of Merge Sort? | Beginner |
| What are the advantages of using Merge Sort? | Intermediate |
| What are the drawbacks of Merge Sort? | Intermediate |
| Explain the stability of Merge Sort. | Intermediate |
| How is Merge Sort different from Quick Sort? | Intermediate |
| What are the applications of Merge Sort? | Intermediate |
| Explain the concept of in-place sorting and whether Merge Sort is in-place. | Advanced |
| What is external sorting, and how is Merge Sort used in it? | Advanced |
| Can Merge Sort be used for sorting large datasets in external memory? | Advanced |
| Advanced | |
| Explain the inversion count problem and how Merge Sort can be used to solve it. | Advanced |
| Discuss the parallelizability of Merge Sort. | Advanced |
| What is the primary drawback of Merge Sort in terms of space complexity? | Advanced |
| How does Merge Sort compare to other sorting algorithms in terms of time complexity? | Advanced |
| Explain the scenario where Merge Sort is not the optimal choice. | Advanced |
| Can Merge Sort be adapted to handle different input distributions? | Advanced |
| How is the pivot element chosen in the Quick Sort algorithm? | Advanced |
Related Articles
- Learn String here
- Dynamic Programming – A Complete Guide
- Learn about Sorting Techniques here
- Wanted to learn about Heap?
- Complete LinkedList
- A Quick Start of RECURSION
- Searching Techniques – A Guide for Amazon SDE Interview Preparation
- Google Interview Preparation for Software Engineer – A Complete Guide to DSA
- STACK Data Structure – A Complete Guide for Beginners