What is a Linked List?
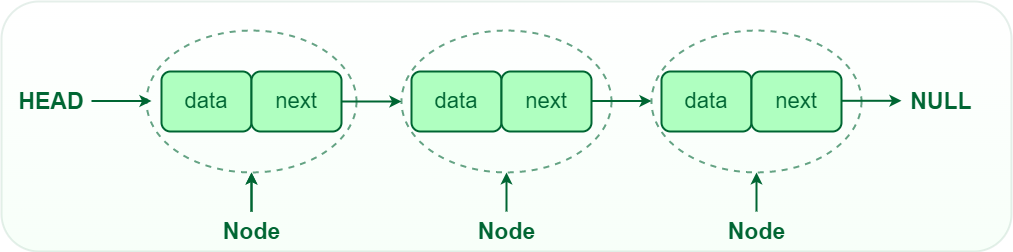
A linked list is a linear data structure that consists of a sequence of elements, each of which contains a reference (or link) to the next element in the sequence. Linked lists are often used to implement dynamic data structures that can grow or shrink as needed. They are commonly used in computer science and programming for various applications.
Why Linked List Data Structure Needed?
Here are a few advantages of a linked list that will help you understand why it is necessary to know:
- Dynamic Data Structure: The size of memory can be allocated or de-allocated at runtime based on the operation of insertion or deletion.
- Ease of Insertion/Deletion: The insertion and deletion of elements are simpler than arrays since no elements need to be shifted after insertion and deletion; just the address needs to be updated.
- Efficient Memory Utilization: As we know, a Linked List is a dynamic data structure; the size increases or decreases as per the requirement, avoiding the wastage of memory.
- Implementation: Various advanced data structures can be implemented using a linked list, such as stacks, queues, graphs, hash maps, etc.
Key Features of Linked Lists
- Dynamic Size: Linked lists can easily grow or shrink in size as elements are added or removed.
- Memory Efficiency: Linked lists can be more memory-efficient than arrays when elements are inserted or deleted frequently.
- Insertions and Deletions: Insertions and deletions can be done at any position in a linked list with relative ease.
- No Fixed Size: Unlike arrays, linked lists do not have a fixed size, making them suitable for dynamic data storage.
Types of Linked Lists
There are several types of linked lists, including:
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
Advantages of Linked Lists:
- Dynamic Nature: Linked lists are used for dynamic memory allocation.
- Memory Efficient: Memory consumption of a linked list is efficient as its size can grow or shrink dynamically according to our requirements, which means effective memory utilization and no memory wastage.
- Ease of Insertion and Deletion: Insertion and deletion of nodes are easily implemented in a linked list at any position.
- Implementation: For the implementation of stacks and queues and for the representation of trees and graphs.
- The linked list can be expanded in constant time.
Disadvantages of Linked Lists:
- Memory Usage: The use of pointers is more in linked lists, making them complex and requiring more memory.
- Accessing a Node: Random access is not possible due to dynamic memory allocation.
- Search Operation Costly: Searching for an element is costly and requires O(n) time complexity.
- Traversing in Reverse Order: Traversing is more time-consuming, and reverse traversing is not possible in singly linked lists.
Applications of Linked List:
Here are some of the applications of a linked list:
- Linear data structures such as stack, queue, and non-linear data structures such as hash maps and graphs can be implemented using linked lists.
- Dynamic memory allocation: We use a linked list of free blocks.
- Implementation of graphs: Adjacency list representation of graphs is the most popular and uses linked lists to store adjacent vertices.
- In web browsers and editors, doubly linked lists can be used to build forward and backward navigation buttons.
- A circular doubly linked list can also be used for implementing data structures like Fibonacci heaps.
Applications of Linked Lists in Real World:
Linked lists find applications in various real-world scenarios:
- The list of songs in the music player is linked to the previous and next songs.
- In a web browser, previous and next web page URLs are linked through the previous and next buttons.
- In the image viewer, the previous and next images are linked with the help of the previous and next buttons.
- Switching between two applications is carried out by using "alt+tab" in Windows and "cmd+tab" in Macbook. It requires the functionality of a circular linked list.
- In mobile phones, we save the contacts of people. The newly entered contact details will be placed at the correct alphabetical order. This can be achieved by a linked list to set contacts at the correct alphabetical position.
- The modifications made in documents are created as nodes in a doubly linked list. We can simply use the undo option by pressing Ctrl+Z to modify the contents. It is done by the functionality of a linked list.
Top 10 Interview Questions on Linked Lists
| Question | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|
| What is a linked list? | Beginner |
| Explain the difference between a singly linked list and a doubly linked list. | Beginner |
| How do you reverse a linked list? | Beginner |
| What is the time complexity of searching for an element in a singly linked list? | Intermediate |
| Explain the concept of a circular linked list. | Intermediate |
| How can you detect a loop in a linked list? | Intermediate |
| Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using a linked list over an array. | Advanced |
| Explain the concept of a skip list and its relation to linked lists. | Advanced |
| How can you optimize a linked list for better performance in specific use cases? | Advanced |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Linked Lists
-
What is a linked list data structure?
Linked lists are most commonly used to handle dynamic data elements. Linked lists consist of nodes, and a node consists of two fields: one for storing data and the other for keeping the reference to the next node. -
What is a linked list example?
A linked list can be assumed as a garland that is made up of flowers. Similarly, a linked list is made up of nodes. Every flower in this particular garland is referred to as a node. In addition, each node points to the next node in this list, and it contains data (in this case, the type of flower). -
Why do we need the linked list data structure?
There are some important advantages to using linked lists over other linear data structures. Unlike arrays, they are resizable at runtime and can be easily inserted and deleted. -
What are linked lists used for?
The linked list is a linear data structure that stores data in nodes. These nodes hold both the data and a reference to the next node in the list. Linked lists are very efficient at adding and removing nodes due to their simple structure. -
What is the difference between an array and a linked list?
There are some differences between them, including the fact that arrays are of fixed size, while linked lists are dynamic and flexible. Linked lists provide faster insertion and deletion operations. -
Why is a linked list preferred over an array?
Linked lists are preferred due to their ability to insert and delete nodes at any point in the list at constant time, dynamic and flexible size, and faster insertion and deletion operations compared to arrays. -
What is the difference between a singly and doubly linked list?
There are some differences between single and double linked lists, including the number of fields in each node and the ability to traverse in both forward and backward directions in a doubly linked list. -
Which is better, an array or a linked list?
There are advantages and disadvantages to both arrays and linked lists. Linked lists are preferred for their dynamic size, ease of insertion/deletion, and more efficient operations. -
What are the limitations of linked lists?
Linked lists have limitations, including more memory usage due to pointers, lack of random access, time-consuming traversing, and costly searching for elements. -
Why are insertion and deletion faster in a linked list?
Insertion and deletion in a linked list are faster because they only require manipulation of node addresses without shifting elements in memory.
Conclusion
There are many advantages of the linked list compared to arrays, despite the fact that they solve similar problems to arrays. We have also discussed the advantages, disadvantages, and applications, and we concluded that linked lists are suitable when you need dynamic storage and fast add/remove operations, but they may not be suitable for querying or searching elements in a large collection of data.
Related Articles
- Learn String here
- Dynamic Programming – A Complete Guide
- Learn about Sorting Techniques here
- Wanted to learn about Heap?
- Complete LinkedList
- A Quick Start of RECURSION
- Searching Techniques – A Guide for Amazon SDE Interview Preparation
- Google Interview Preparation for Software Engineer – A Complete Guide to DSA
- STACK Data Structure – A Complete Guide for Beginners