What is Array?
An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together. This makes it easier to calculate the position of each element by simply adding an offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array (generally denoted by the name of the array).
Topics in Array
-
What is Array?
An array is a collection of elements, each identified by an index or a key. It is a data structure used to store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type.
-
Introduction to Array
Arrays are commonly used in computer programs to organize and manage data. They provide quick access to data elements and are used for various applications.
- Advantages and Disadvantages
Arrays have advantages such as fast element access, but they also have disadvantages like a fixed size. Understanding when to use arrays is important in software development.
Why Array Data Structures are Needed?
Assume there is a class of five students, and if we have to keep records of their marks in the examination, then we can do this by declaring five variables individually and keeping track of records. However, what if the number of students becomes very large? It would be challenging to manipulate and maintain the data.
What it means is that we can use normal variables (v1, v2, v3, ...) when we have a small number of objects. But if we want to store a large number of instances, it becomes difficult to manage them with normal variables. The idea of an array is to represent many instances in one variable.
Types of Arrays:
There are majorly two types of arrays:
- One-dimensional array (1-D arrays): You can imagine a 1D array as a row, where elements are stored one after another.
- Two-dimensional array: 2-D Multidimensional arrays can be considered as an array of arrays or as a matrix consisting of rows and columns.
- Three-dimensional array: A 3-D Multidimensional array contains three dimensions, so it can be considered an array of two-dimensional arrays.
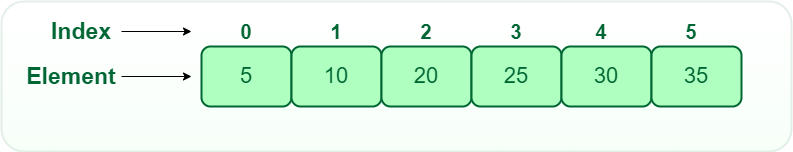
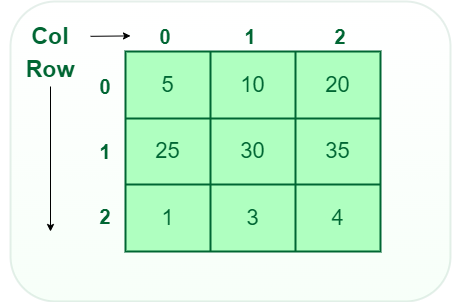
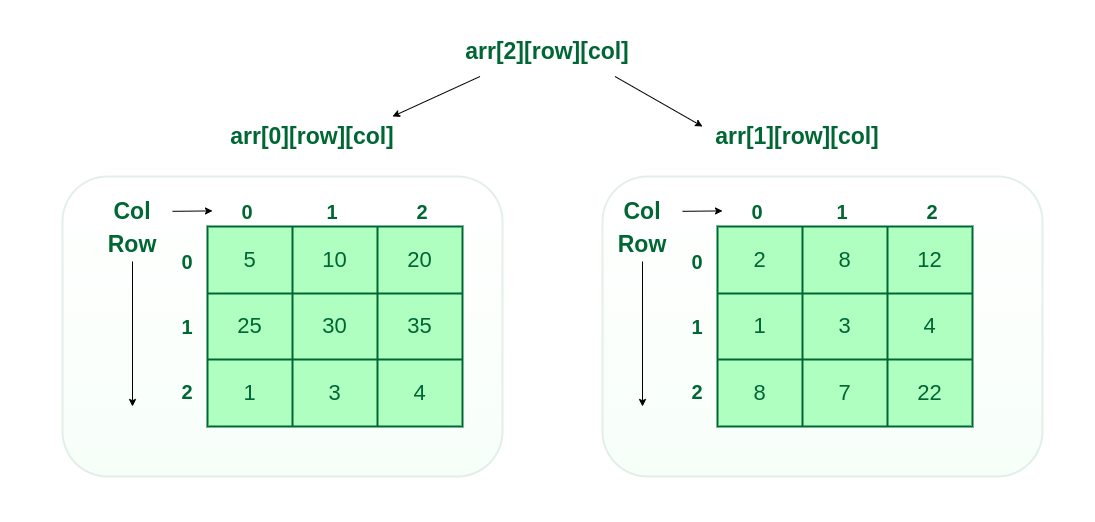
Types of Array Operations:
- Traversal: Traverse through the elements of an array.
- Insertion: Inserting a new element in an array.
- Deletion: Deleting an element from the array.
- Searching: Search for an element in the array.
- Sorting: Maintaining the order of elements in the array.
Advantages of Using Arrays:
- Arrays allow random access to elements. This makes accessing elements by position faster.
- Arrays have better cache locality which makes a significant difference in performance.
- Arrays represent multiple data items of the same type using a single name.
- Arrays store multiple data of similar types with the same name.
- Array data structures are used to implement other data structures like linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs, etc.
Disadvantages of Arrays:
- As arrays have a fixed size, once the memory is allocated to them, it cannot be increased or decreased, making it impossible to store extra data if required. An array of fixed size is referred to as a static array.
- Allocating less memory than required to an array leads to a loss of data.
- An array is homogeneous in nature, so a single array cannot store values of different data types.
- Arrays store data in contiguous memory locations, which makes deletion and insertion very difficult to implement. This problem is overcome by implementing linked lists, which allow elements to be accessed sequentially.
Applications of Arrays:
- They are used in the implementation of other data structures such as array lists, heaps, hash tables, vectors, and matrices.
- Database records are usually implemented as arrays.
- It is used in lookup tables by computers.
- It is used for different sorting algorithms such as bubble sort, insertion sort, merge sort, and quick sort.
Frequently Asked Questions on Arrays
Question Difficulty Level What is an array? Beginner How do you access elements in an array? Beginner What are the advantages of using arrays? Intermediate What are the disadvantages of arrays? Intermediate How do you find the length of an array? Beginner Explain the concept of multi-dimensional arrays. Intermediate What is the difference between an array and a linked list? Intermediate How do you reverse an array in-place? Intermediate Explain the concept of dynamic arrays. Intermediate How do you remove duplicates from an array? Intermediate What is the time complexity of various array operations? Advanced How do you implement a resizable array? Advanced Explain the concept of sparse arrays. Advanced How do you rotate an array to the right by a given number of positions? Advanced What is a jagged array? Advanced Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Arrays
- What is an array in data structure with example?
An array is a collection of items of the same data type stored at contiguous memory locations. Ex. int arr[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
- Why array is a data structure?
Arrays store elements of the same type; they are classified as homogeneous data structures. They can store numbers, strings, characters, boolean values (true and false), objects, and so on.
- What data structure is an array?
An array is a linear data structure that stores similar elements in contiguous memory locations.
- What are the types of arrays?
There are majorly two types of arrays:
- One-dimensional array
- Multidimensional array
- How is data stored in an array?
An array is a collection of items of the same data type stored at contiguous memory locations, and the elements are stored one after another in memory. An array uses an index system starting at 0 and going to (n-1), where n is its size.
- Difference between array and structure?
The structure can contain variables of different types, but an array only contains variables of the same type.
- What are the limitations of an array?
An array is a collection of items of the same data type. That means, in an integer array only integer values can be stored, while in a float array only floating values, and character arrays can have only characters. Thus, no array can have values of two data types.
- What are the advantages of an array?
There are multiple advantages of the array data structure, and some of them are:
- Arrays allow random access to elements. This makes accessing elements by position faster.
- Arrays store multiple data of similar types with the same name.
- Array data structures are used to implement other data structures like linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs, etc.
- What is the purpose of using arrays?
An array is used when several variables of the same type need to be used, and it can be defined as a sequence of objects of the same type.
- What is a multidimensional array?
A multi-dimensional array can be termed as an array of arrays that stores homogeneous data in tabular form. Data in Multidimensional Arrays are stored in row-major order.
Conclusion
After the discussion, we concluded that arrays are a simple method of accessing elements of the same type by grouping them, and we can find the elements efficiently by their indexes and can perform different operations using them. Thus, they are more efficient when it comes to memory allocation and should be used in all modern programming languages. So, this becomes a favorite topic for the perspective of the interview, and most of the companies generally asked about the problems on the array. For all these reasons, we must have a good knowledge of it.
Related Articles
- Learn String here
- Dynamic Programming – A Complete Guide
- Learn about Sorting Techniques here
- Wanted to learn about Heap?
- Complete LinkedList
- A Quick Start of RECURSION
- Searching Techniques – A Guide for Amazon SDE Interview Preparation
- Google Interview Preparation for Software Engineer – A Complete Guide to DSA
- STACK Data Structure – A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Advantages and Disadvantages